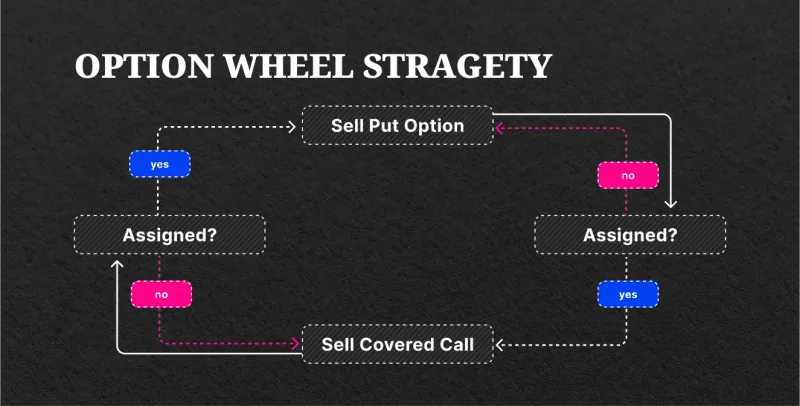
The options wheel strategy is an income-generating technique that entails selling put options, the prospect of owning stock, and selling covered calls until the shares are called away or the transaction is closed. This strategy has grown in favor among investors looking to generate income both before and during their stock ownership.
The wheel strategy's option primary goal is not to acquire and hold shares. Instead, it focuses on producing credit on a steady basis by selling short-put options. However, selling these put options prior to purchasing the shares reduces the overall cost basis of the position over time.
If you are issued shares, the technique entails writing covered calls to create extra income until the net cost basis falls below the current stock price, allowing you to liquidate the position at a profit.
In essence, the options wheel technique is a proactive type of passive investing that provides investors with a consistent source of income. It's ideal for stock investors who want to make a smooth move into options trading.
The Options Wheel Strategy Consists of Two Major Steps:
1. Selling a cash-secured put option: This entails receiving a credit for the put option contract's premium amount. These options are typically offered below the current stock price and are called out-of-the-money.
2. Selling a covered call if you end up owning the stock: If you are assigned the stock as a result of selling the short put, you must be prepared to buy 100 shares per contract.
Once you have the shares, you can continue the technique by selling covered calls at a price higher than the stock's current price. The premiums earned from selling both puts and covered calls are used to support these calls.
The covered calls can be sold indefinitely until the stock's net cost falls below its current share price. If the stock price rises modestly, the short call will expire out of the money. This allows you to keep the entire premium and sell another call option for the next expiration, lowering your overall cost basis.
Finally, you have the option of allowing the shares to be called away or selling them for a profit.
The options wheel strategy can be used indefinitely, or until the call option expires in the money and the shares are called away. At this point, you have the opportunity to restart the process by selling a fresh short put option.
Executing the Wheel Strategy Involves Several Key Considerations:
1. Careful Selection: It's crucial to emphasize that when employing the wheel strategy, you should exclusively sell put options on stocks you genuinely intend to hold at a price that you find acceptable for owning those shares.
2. Potential Outcomes: There are two possible scenarios when implementing the wheel strategy:
- The put option expires without value, and you retain the entire premium. This is typically the preferred outcome.
- The put option gets assigned, indicating that you acquire the shares. Subsequently, you engage in selling covered calls until either the call option is assigned, or you make the decision to sell the stock.
3. Desire for Stock Appreciation: If you end up holding the assigned shares, it is desirable for the stock price to appreciate over the long term. This allows you to benefit from capital gains while also generating recurring income through the sale of covered calls.
4. Selling a Put Option: The initial step involves selling a short put option. You have flexibility in choosing the strike price, and many investors employ this as a means of generating income while effectively setting a limit order for purchasing the underlying stock at a price they find favorable.
5. Outcome of the Short Put: If, at the option's expiration, the underlying stock's price exceeds the strike price of the short put, the contract becomes worthless, and you retain the premium received for selling the put.
6. Continuation and Adjustments: You can continue this process for as long as you prefer, and you possess the ability to adjust the strike price either upward or downward based on your evolving market perspectives or changing circumstances.
Additionally, rolling the short put can be an effective tactic to potentially postpone assignments while collecting additional premiums. This extra premium can boost profits if the stock price stages a recovery or reduce the net cost basis of the stock if you end up being assigned.
Sell a Covered Call
In the event that the stock's price is below the strike price at expiration, you will be assigned 100 shares per contract at the strike price. Nonetheless, the position's cost basis is mitigated by the net credit obtained from selling put options.
For instance, if you decide to sell a put option with a $100 strike price and receive a premium of $5.00, your effective cost for the stock would be $95 if you are assigned the shares.
In the case of a short put, keep in mind that you'll be obligated to purchase 100 shares per contract if the assignment occurs. Therefore, you need to have sufficient funds in your account to cover the purchase.
When selling a put with a $100 strike price, you should have a minimum of $10,000 available in your account.
Once you acquire the stock, you can proceed to sell a covered call. Selling a covered call also generates income in the form of a premium and is akin to collecting rent for owning the stock. This income can be supplemented by dividends earned along the way.
Similar to short puts, you have the option to roll a call option to potentially collect more premium, extend the trade, and sell at a higher strike price. Once again, the premiums collected from selling options continue to lower the overall cost basis of the position.
It's important to note that the closer the short call's strike price is to the current stock price, the more premium you will receive, but there is a higher likelihood that the option will expire in the money (you can use delta to assess probabilities).
Additionally, option contracts with longer expiration dates offer higher premiums but also carry a greater likelihood of expiring in-the-money. These factors should be considered when selecting a call option.
Option Wheel Strategy Example
Now, let's consider an example of the option wheel strategy. Suppose a stock is currently trading at $67, and you are willing to acquire at least 100 shares at $65. You can opt to sell a cash-secured put with a $65 strike price.
The longer the expiration date of the contract, the more premium you'll collect because the option will have greater extrinsic value.
If, at expiration, the stock price is above the strike price, you can repeat the process with a later expiration date. Conversely, if the stock drops to $65 or below, you may be assigned shares at $65. The premiums collected from any put options will reduce your cost basis.
Once you become the owner of the stock, you can proceed to sell a call option with a $68 strike price, further lowering your cost basis. In the event that the stock is not called away because it does not reach the call option's strike price, you can repeat the call selling process in the following month.
However, if the stock exceeds the call option's strike price, you are obligated to sell the shares at $68, regardless of the stock's current market price.
Important Considerations
It's important to remember that the option wheel strategy is most suitable for stocks you genuinely want to own, and it aligns with your bullish outlook over the short, medium, or long term, depending on your preference. When you sell a put option to initiate stock ownership, you earn income while awaiting potential assignment.
Keep in mind that there's always the chance that an assignment may not occur, and you won't end up owning the stock. Nonetheless, you will retain the premium received for selling the put.
Lastly, be aware that the option wheel strategy can require a significant allocation of capital, so it's essential to ensure that it fits within your overall portfolio and risk management strategy.
Also, consider your long-term outlook for the stock since the option wheel strategy can extend over weeks, months, or even years depending on the stock's price movement.
Dive deeper into the dynamics of financial markets with our Technical Analysis Crash Course, perfect for enhancing your trading skills and strategy development.